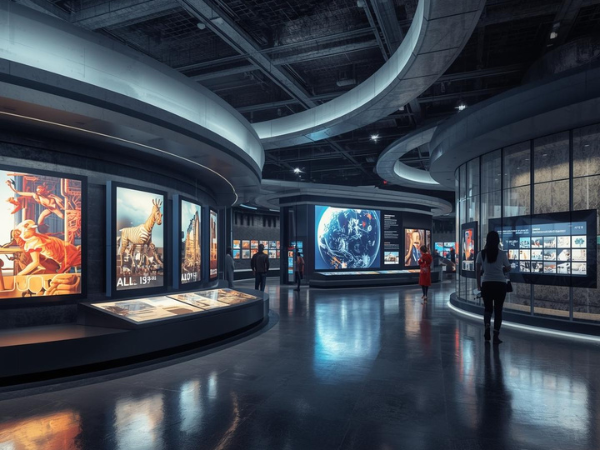
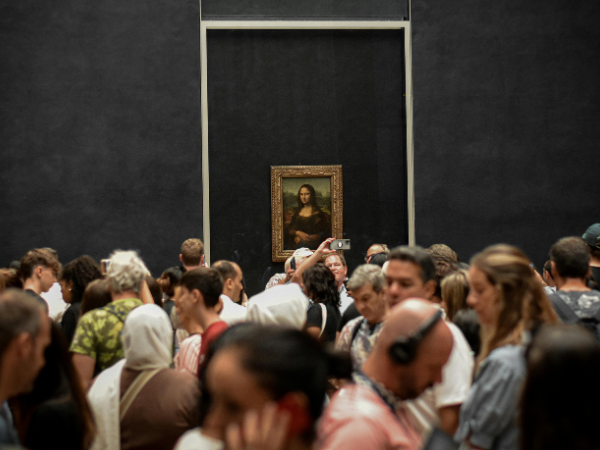
Virtual museums are redefining how audiences experience art and culture. By blending advanced technology with timeless masterpieces, they make exhibitions accessible to anyone, anywhere. In 2026, virtual museums are not just digital replicas of galleries—they are immersive, interactive spaces where history, creativity, and innovation converge.
The Evolution of Virtual Museums
Virtual museums have grown from simple online catalogs into fully immersive experiences. They now offer dynamic environments that rival physical galleries.
Key stages in their evolution:
- Early Online Archives – Basic image collections of artworks.
- Interactive Websites – Multimedia tours with audio guides.
- Virtual Reality Galleries – Immersive 3D spaces replicating museums.
- Augmented Reality Exhibits – Overlaying art into real‑world settings.
- Metaverse Integration – Social, interactive art communities online.
This evolution shows how technology has expanded the reach of cultural institutions. Virtual museums are no longer secondary experiences—they are primary destinations for global audiences.
Why Technology Enhances the Museum Experience
Technology allows museums to present art in ways that were previously impossible. It enriches storytelling and deepens audience engagement.
Ways technology enhances museums:
- High‑Resolution Imaging – Zoom into details of masterpieces.
- 3D Reconstructions – Explore ancient artifacts virtually.
- Interactive Displays – Engage with multimedia storytelling.
- AI Curation – Personalized recommendations for visitors.
- Global Access – View collections from anywhere.
By integrating technology, museums create experiences that are both educational and entertaining. Visitors gain deeper insights into art while enjoying interactive exploration.
Accessibility and Inclusivity in Virtual Museums
Virtual museums break barriers of geography, cost, and mobility, making art accessible to all.
Accessibility benefits of virtual museums:
- Global Reach – Audiences worldwide can access collections.
- Cost‑Free Entry – Many virtual museums are free to explore.
- Language Options – Multilingual guides for diverse audiences.
- Disability Access – Features like audio descriptions and captions.
- Flexible Timing – Available 24/7 without restrictions.
These features ensure inclusivity, allowing people from different backgrounds to engage with culture. Virtual museums democratize art, making masterpieces available to everyone.
Famous Institutions Leading Virtual Innovation
Several world‑renowned museums are pioneering virtual exhibitions, setting standards for others.
Examples of leading institutions:
- The Louvre – Virtual tours of iconic works like the Mona Lisa.
- The British Museum – Online access to global artifacts.
- The Smithsonian – Interactive exhibits across disciplines.
- The Vatican Museums – Digital tours of historic collections.
- The Metropolitan Museum of Art – Immersive online galleries.
These institutions prove that virtual museums can complement physical spaces while expanding their reach. Their innovation inspires smaller museums to adopt similar practices.
Interactive Features That Engage Visitors
Virtual museums thrive on interactivity, turning passive viewing into active participation.
Popular interactive features:
- Virtual Tours – Guided journeys through collections.
- Live Q&A Sessions – Direct engagement with curators.
- Gamification – Quizzes and challenges for visitors.
- Social Sharing – Integration with social media platforms.
- Customizable Avatars – Personalized exploration in virtual spaces.
These features make virtual museums engaging and memorable. They encourage repeat visits and foster deeper connections between audiences and art.
Challenges Facing Virtual Museums
Despite their advantages, virtual museums face obstacles that must be addressed.
Common challenges include:
- Technical Limitations – High‑quality VR requires advanced hardware.
- Authenticity Concerns – Replicating the aura of physical art.
- Funding Issues – Maintaining digital platforms can be costly.
- Digital Fatigue – Overexposure to screens reduces engagement.
- Security Risks – Protecting digital collections from piracy.
Addressing these challenges is crucial for sustainability. Museums must balance innovation with authenticity to maintain credibility.
Artists Thriving in Virtual Museum Spaces
Virtual museums provide new opportunities for artists to showcase their work globally.
Examples of thriving artists:
- Refik Anadol – AI‑driven immersive installations.
- Beeple – Digital art pioneer through NFTs.
- TeamLab – Interactive collective blending art and tech.
- Marina Abramović – Performance art adapted for virtual audiences.
- David Hockney – Traditional art reimagined digitally.
These artists demonstrate how virtual museums expand creative possibilities. They prove that digital spaces can be fertile ground for innovation.
The Future of Virtual Museums in 2026 and Beyond
Virtual museums are evolving rapidly, with new technologies shaping their future.
Future trends include:
- AI‑Curated Exhibitions – Personalized art journeys.
- Metaverse Integration – Social, immersive art communities.
- Hybrid Models – Combining physical and digital experiences.
- Sustainability Focus – Reducing carbon footprint through digital events.
- Global Collaborations – Artists and institutions working across borders.
The future promises even greater accessibility and innovation. Virtual museums will continue to redefine how audiences experience timeless masterpieces.
Final Reflections: Technology Meets Timeless Art
Virtual museums represent a fusion of tradition and innovation. They preserve cultural heritage while embracing modern technology.
Key reflections on virtual museums:
- Accessibility – Art for everyone, everywhere.
- Innovation – Expanding creative possibilities.
- Resilience – Adapting to global challenges.
- Community – Connecting audiences worldwide.
- Sustainability – Eco‑friendly cultural engagement.
Ultimately, virtual museums are not replacements for traditional galleries—they are powerful complements. They ensure that timeless masterpieces remain relevant in a digital age, bridging the gap between past and future.